Welcome to the “Beginner’s Guide To Managing Alligator Weed In Aquatic Environments.” In this helpful guide, you’ll discover practical strategies to identify, control, and manage the invasive alligator weed that threatens your local waterways. You’ll gain essential knowledge about the various methods to keep these resilient plants in check, ensuring that your aquatic environment remains healthy and balanced. Whether you’re a newcomer to this challenge or just looking for effective solutions, this guide is your key to mastering alligator weed management.
Beginner’s Guide to Managing Alligator Weed in Aquatic Environments
Have you ever wondered how to tackle the pesky issue of alligator weed in your ponds or lakes? You’re not alone! Managing alligator weed, especially in aquatic environments, can seem like a daunting task. Don’t worry, though—this beginner’s guide will walk you through everything you need to know to keep your water bodies weed-free.
What is Alligator Weed?
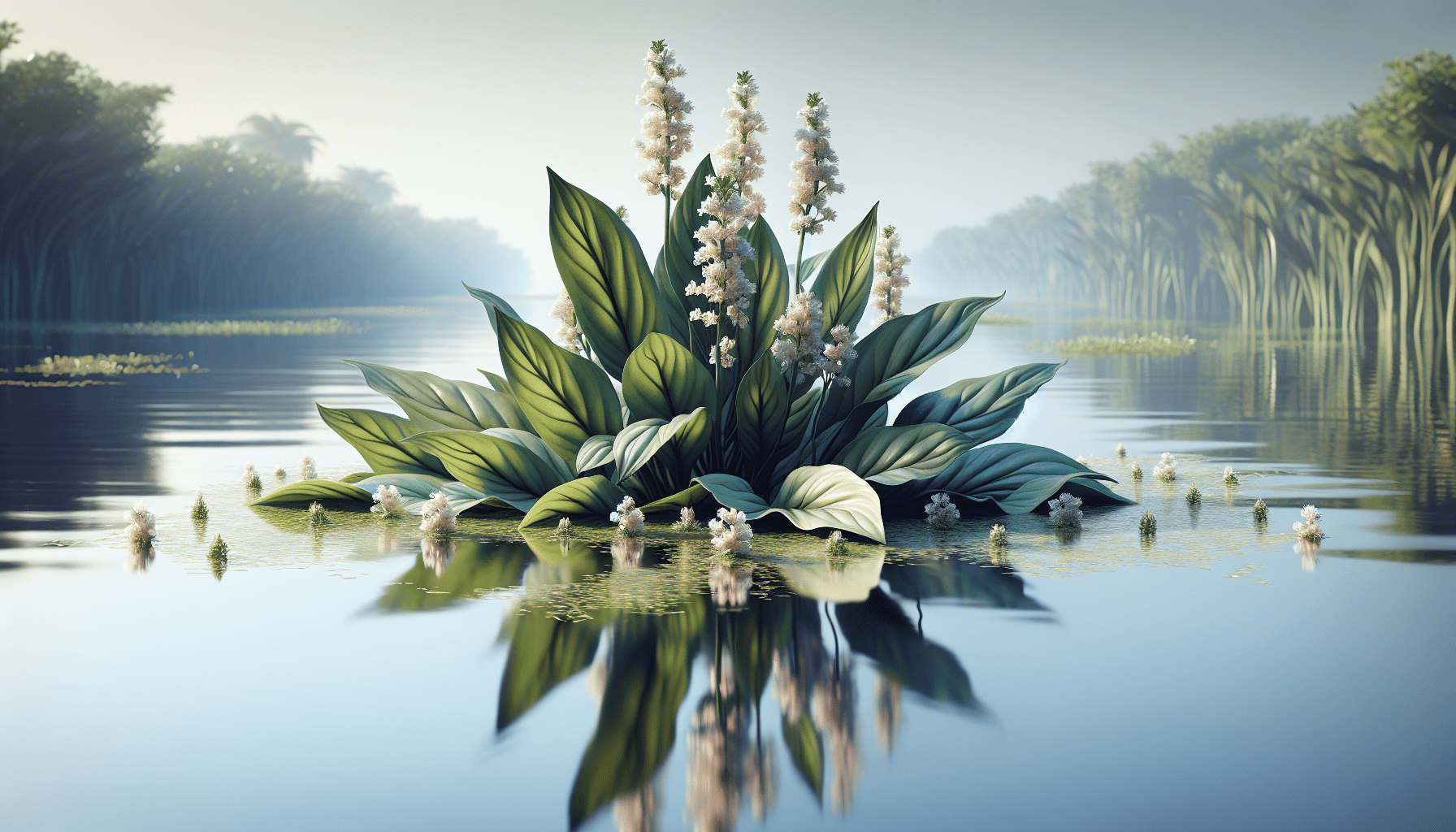
Alligator weed (Alternanthera philoxeroides) is an invasive plant species native to South America. It’s notorious for its aggressive growth habits and ability to clog waterways, create dense mats on water surfaces, and disrupt native ecosystems.
Characteristics of Alligator Weed
Alligator weed can often be identified by its dark green, waxy leaves and hollow stems. The plant typically forms extensive mats and has small white flowers that bloom from April to October.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Origin | South America |
| Growth Habit | Aggressive, forms dense mats |
| Leaves | Dark green, waxy |
| Stems | Hollow |
| Flowers | Small, white, bloom April-October |
Why is Alligator Weed a Problem?
Environmental Impact
One of the biggest concerns with alligator weed is its significant environmental impact. It can outcompete native plants, reduce biodiversity, and alter habitats by displacing beneficial plant species and altering water flows.
Economic Impact
In addition to environmental issues, alligator weed can also result in substantial economic consequences. It can hinder irrigation, obstruct recreational activities, and increase costs for waterway maintenance.
| Impact Type | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Environmental | Reduced biodiversity, habitat alteration |
| Economic | Increased maintenance costs, obstructed activities |

How Does Alligator Weed Spread?
Understanding how alligator weed spreads is vital to managing it effectively. The plant propagates both sexually through seeds and vegetatively through fragmentation. Even small pieces of the plant can take root and grow, making eradication challenging.
Modes of Spread
- Water Currents: Fragments can float and take root downstream.
- Animal Movement: Aquatic birds and animals can carry fragments.
- Human Activity: Boat traffic, fishing gear, and equipment can spread the weed.
Identifying Alligator Weed
Early identification is crucial for controlling alligator weed. Familiarize yourself with the plant’s distinctive features to ensure timely intervention.
Visual Identification Tips
- Look for mats of dark green, waxy leaves floating on the water surface.
- Check for hollow stems that may snap easily.
- Note the presence of small white flowers, particularly during blooming months.

Methods of Control
Once identified, you’ll need to choose a management strategy. There are several options at your disposal, ranging from mechanical to chemical and biological methods.
Mechanical Control
Mechanical methods involve physically removing or cutting the weed. This can be achieved through tools like rakes, underwater mowers, and harvesters.
Pros and Cons of Mechanical Control
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Immediate results | Labor-intensive, may need frequent repetition |
| Non-chemical, eco-friendly | Expensive equipment, potential for regrowth |
Chemical Control
Selective herbicides can help manage alligator weed effectively. These chemicals target the invasive species while sparing native plants. However, their use should be approached with caution to avoid environmental damage.
Types of Herbicides
- Glyphosate: Non-selective herbicide effective against alligator weed.
- 2,4-D: Selective herbicide, primarily used in agricultural settings.
Pros and Cons of Chemical Control
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Effective over large areas | Potential environmental impact |
| Long-lasting results | Requires careful application and permits |
Biological Control
Biological control involves using natural predators or pathogens to manage the alligator weed population. This method offers a sustainable, long-term solution but requires time to be effective.
Biological Agents
- Alligator Weed Flea Beetles (Agasicles hygrophila): Feeds exclusively on alligator weed, reducing its growth.
- Stem Borers (Arcola malloi): Larvae bore into stems, causing structural damage.
Pros and Cons of Biological Control
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Sustainable and eco-friendly | Slow initial results |
| Potentially cost-effective in the long run | Limited control options currently available |
Integrated Weed Management (IWM)
For the best outcomes, consider an integrated weed management (IWM) approach. IWM combines multiple control methods to offer comprehensive, sustainable weed management solutions.
Steps for IWM
- Assessment: Identify the extent of the infestation and the particular needs of your environment.
- Strategy Development: Combine mechanical, chemical, and biological methods based on the assessment.
- Implementation: Execute the planned control measures.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor the situation to assess the effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.

Safety Precautions
Handling Chemicals
When using chemical herbicides, always follow safety guidelines and read the labels. Use personal protective equipment (PPE) to minimize risk.
| PPE | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Gloves | Protection from chemical exposure |
| Goggles | Eye protection |
| Masks | Respiratory protection |
Equipment Safety
Operating mechanical equipment can be hazardous. Ensure all operators are trained and follow safety protocols.
| Equipment | Safety Tip |
|---|---|
| Rakes | Ensure secure footing to avoid falling |
| Harvesters | Never operate alone, have a spotter |
Community Engagement
Managing alligator weed isn’t just a personal endeavor—it requires community effort. Engaging local stakeholders, government agencies, and environmental organizations can significantly amplify control measures.
Building Awareness
Raise awareness about the issues and control measures through community meetings, flyers, and social media campaigns. The more people know, the better equipped you’ll be as a community to tackle the weed problem.
Volunteer Programs
Organize community cleanup and control events. Volunteer programs can offer manpower for manual removal methods and foster a sense of collective responsibility.
Case Studies
Learning from successful case studies can provide insights and practical advice for managing alligator weed.
Case Study 1: Lake Kyoga, Uganda
In Lake Kyoga, a community-based approach was employed. Local fishermen were trained and equipped with manual tools for regular weed removal. Over time, the weed coverage significantly reduced, and fish populations began to recover.
Case Study 2: Louisiana, USA
Louisiana faced a severe alligator weed infestation in its waterways. Implementing an integrated approach, the state used mechanical harvesters for immediate removal, followed by the introduction of alligator weed flea beetles. This combination controlled the weed effectively while minimizing the use of herbicides.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular Inspections
Regular inspections are crucial for early detection and management. Schedule periodic checks of your water bodies to catch new growth before it becomes unmanageable.
Record Keeping
Keep detailed records of control measures, herbicide applications, and any observed changes. Documenting these details will help fine-tune your control efforts.
| Date | Method | Observations |
|---|---|---|
| 01/15/2023 | Mechanical | Successful removal, minor regrowth noticed |
| 02/05/2023 | Chemical | Effective, reduced spread |
| 03/10/2023 | Biological | Flea beetle population thriving, alligator weed under control |

Final Thoughts
Managing alligator weed in aquatic environments is not a one-time task—it’s an ongoing effort that requires knowledge, commitment, and community involvement. By understanding the plant, utilizing various control methods, and engaging your community, you can successfully manage and even eradicate this invasive species from your water bodies.
Feel free to refer back to this guide whenever you need a quick refresher or when you face challenges in your weed management journey. Together, we can keep our rivers, lakes, and ponds healthy and thriving for future generations.
