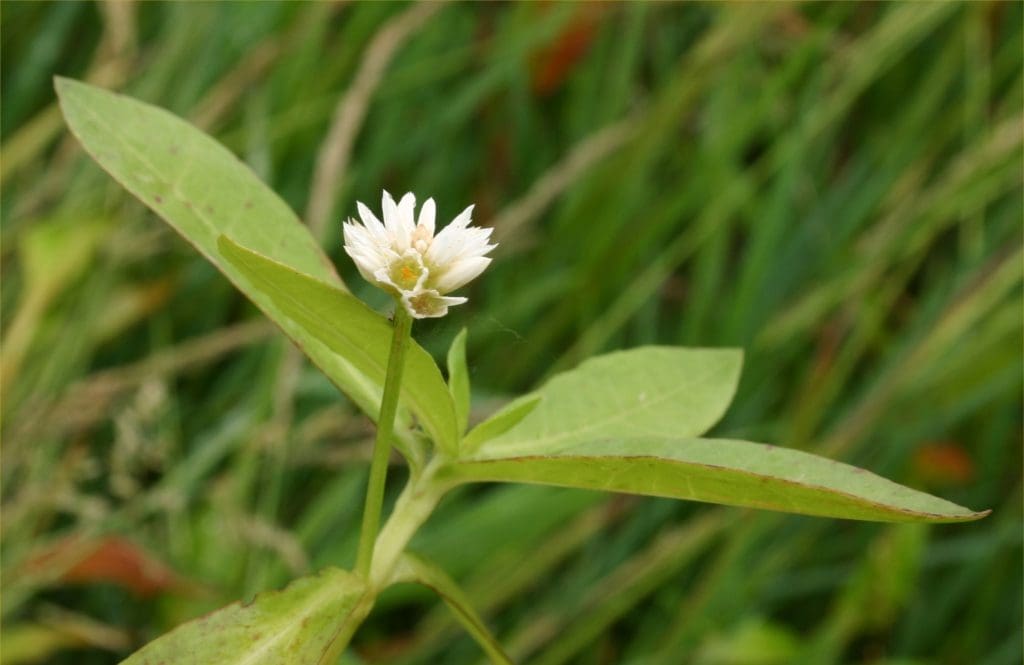
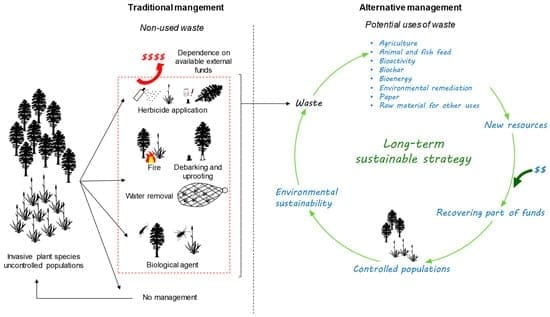
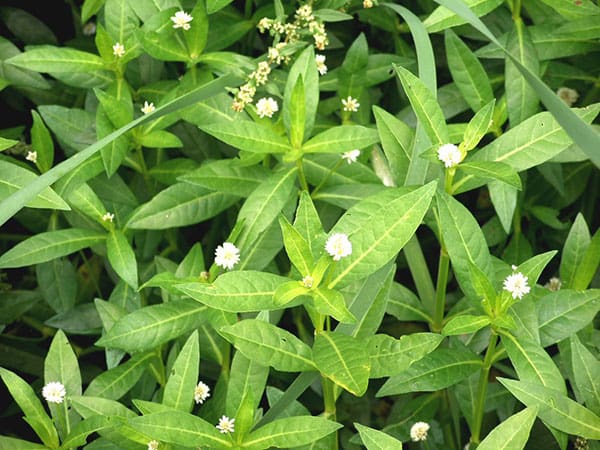
Are you concerned about the spread of alligator weed in your community? It’s a worry many communities share as this invasive plant can wreak havoc on local ecosystems, waterways, and landscapes if not properly managed. While tackling alligator weed might seem daunting, understanding its nature and how to prevent it from spreading can make a significant difference. This guide is designed to provide you with practical steps to help curb the spread of alligator weed in your area.

Understanding Alligator Weed
What is Alligator Weed?
Alligator weed (Alternanthera philoxeroides) is a highly invasive perennial plant native to South America. This robust and pesky plant usually thrives in aquatic environments like rivers, lakes, and wetlands but can also spread to farmland and other areas with sufficient moisture. Alligator weed is known to form dense mats that obstruct waterways, displace native vegetation, and disturb local ecosystems.
Why is Alligator Weed a Problem?
Alligator weed poses several problems due to its aggressive growth and resilience. Its dense mats can block waterways, making navigation difficult and disrupting water flow. Moreover, it can negatively impact biodiversity by outcompeting native plants, thereby threatening local wildlife habitats. Lastly, infestations can affect agricultural efficiency and operations by overrunning pastures and crop fields.
Identifying Alligator Weed
Physical Characteristics
Proper identification is crucial to control alligator weed. Here are some key characteristics to help you recognize it:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Leaves: | Opposite, elliptical, up to 10 cm long, waxy and green |
| Stems: | Hollow, can be reddish, can float or trail along the ground |
| Flowers: | Small, white, in clusters (like clover), bloom all year |
| Roots: | Extensive root systems, can grow in water and soil |
Common Look-Alikes
Alligator weed can be mistaken for other plants. Ensure you don’t confuse it with these look-alikes:
| Look-Alike | Distinguishing Feature |
|---|---|
| Water Primrose | Bright yellow flowers, not white |
| Smartweed | Lance-shaped leaves, pink flower spikes |
| Knotweed | Small, knot-like flower clusters along stem |
How Alligator Weed Spreads
Natural Dispersal
Alligator weed spreads through several natural mechanisms:
- Vegetative Fragments: Even small stem or root pieces can establish new infestations if they break off and spread to new locations.
- Water Currents: Flowing water can carry plant fragments downstream, leading to new colonies.
- Animals: Birds and other wildlife can inadvertently transport fragments to new areas.
Human Activities
Human actions often accelerate the spread of alligator weed:
- Boating: Boats moving through infested waters can cut and carry plant fragments.
- Agriculture: Equipment, soil movement, and irrigation can contribute to its spread.
- Aquarium Disposal: Improper disposal of aquarium plants can introduce alligator weed to new environments.
Preventing the Spread of Alligator Weed
Community Awareness
Raising community awareness is essential in preventing the spread of alligator weed. Here’s how you can get started:
- Educational Workshops: Host workshops and seminars to educate residents about identifying and managing alligator weed.
- Publications: Distribute flyers, brochures, and newsletters with information on prevention and control.
- Social Media: Use social media platforms to share educational content and encourage community participation.
Best Practices for Individuals
Individuals play a critical role in preventing the spread of alligator weed. Here are some guidelines:
- Inspect and Clean Boats and Equipment: Regularly check and clean boats, trailers, and fishing gear to remove plant fragments.
- Proper Disposal: Never dispose of unwanted plants into local waterways or wild areas.
- Stay Informed: Learn how to identify alligator weed and report any sightings to local authorities.
Action Plan for Local Government
Local governments can implement policies and programs to manage and prevent the spread of alligator weed:
- Surveys and Monitoring: Conduct regular surveys to monitor and map infestations.
- Regulations: Create and enforce regulations that prevent the transport of alligator weed.
- Control Programs: Implement integrated management programs that include mechanical removal, biological control, and chemical treatments.

Alligator Weed Control Methods
Mechanical Control
Mechanical control involves physically removing the plant from infested areas. Here are some methods and their effectiveness:
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hand Pulling | Manually removing plants and roots | No chemicals | Labor-intensive |
| Cutting/Mowing | Cutting stems above water/ground surface | Immediate results | May not remove roots |
| Dredging | Using machinery to remove plants from water bodies | Effective for large areas | High cost and disturbance to habitat |
Biological Control
Biological control uses natural enemies to reduce weed populations. Potential biological agents include:
- Insects: Specific beetles and moths have been introduced in some regions to feed on alligator weed leaves and stems.
- Pathogens: Certain fungi and diseases can be deployed to infect and weaken the weed.
Chemical Control
Chemical control involves using herbicides to kill the weed. It is often used as part of an integrated approach. Here’s a look at common herbicides and their efficacy:
| Herbicide | Application Method | Effectiveness | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glyphosate | Spot treatment, foliar spray | Very effective | Low if used correctly |
| Imazapyr | Foliar spray | Effective | Can affect non-target species |
Integrated Management
The most effective approach often combines mechanical, biological, and chemical methods tailored to local conditions. This integrated management strategy ensures long-term control and mitigates the negative impacts of any single control method.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Establishing Monitoring Programs
Regular monitoring is essential to assess the success of control efforts and detect new infestations early. Communities can establish monitoring programs by:
- Setting up Patrols: Regular patrols of waterways and infested areas.
- Citizen Reporting: Encouraging community members to report sightings.
Evaluating Control Efforts
It’s crucial to evaluate control efforts to ensure they are achieving desired outcomes. Use the following metrics:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduction in Coverage | Decrease in area covered by alligator weed over time |
| Biodiversity Increases | Recovery of native plant and animal species |
| Waterway Quality | Improvement in water quality and flow |

Engaging the Community
Building a Volunteer Network
Volunteers can significantly bolster your efforts to control alligator weed. Consider these strategies to build a robust volunteer network:
- Recruitment Drives: Regularly host drives to recruit new volunteers.
- Training Programs: Provide training to ensure volunteers can identify and manage alligator weed effectively.
- Recognition Events: Hold events to recognize and celebrate the contributions of volunteers.
Collaborating with Local Organizations
Partnering with local organizations can amplify your efforts. Potential partners include:
- Environmental Groups: Collaborate on awareness campaigns and control efforts.
- Schools and Universities: Engage students in research and monitoring activities.
- Businesses: Seek sponsorships and in-kind support for control activities.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges
Several challenges may arise in the effort to control alligator weed:
- Fragmentation: Small plant fragments can quickly lead to new infestations.
- Access Issues: Dense infestations can be difficult to access for control efforts.
- Public Awareness: Ensuring broad public awareness and cooperation can be tough.
Practical Solutions
Address these challenges with practical solutions:
- Use Fragment Barriers: Install barriers in waterways to capture and remove plant fragments.
- Employ Specialized Equipment: Use equipment designed for hard-to-access areas.
- Leverage Media Campaigns: Use local media to spread awareness and educate the public.

Success Stories
Case Study: Effective Community Action
Consider a community that successfully managed an alligator weed infestation through a well-coordinated action plan. Volunteers conducted regular cleanups, local authorities implemented strict regulations, and educational programs kept the public informed. As a result, the infestation was significantly reduced, waterways were restored, and native biodiversity began to flourish again.
Expert Recommendations
Experts recommend taking a proactive approach to manage invasive species like alligator weed. Here’s some advice from professionals:
- Stay Vigilant: Regular monitoring is key.
- Be Comprehensive: Combine multiple control methods for best results.
- Engage the Community: Broad participation ensures more effective control.
Conclusion
Preventing the spread of alligator weed requires a concerted and collaborative effort within the community. By understanding the nature of this invasive species, taking decisive actions, and promoting community involvement, you can protect your local ecosystems and maintain the health of your waterways. Remember, every little effort counts in safeguarding our environment from invasive plants like alligator weed. By staying informed and proactive, you can make a significant difference.