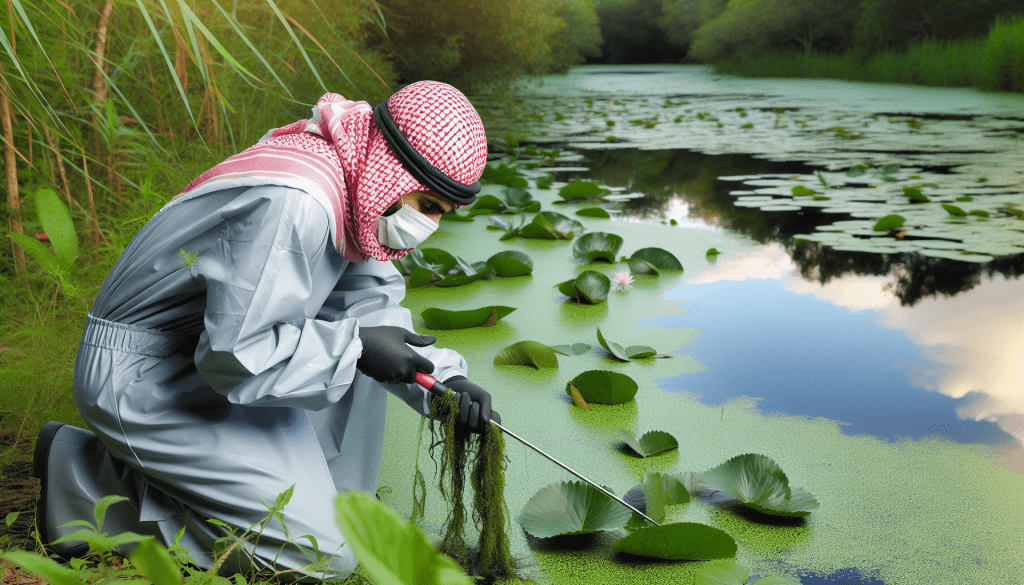
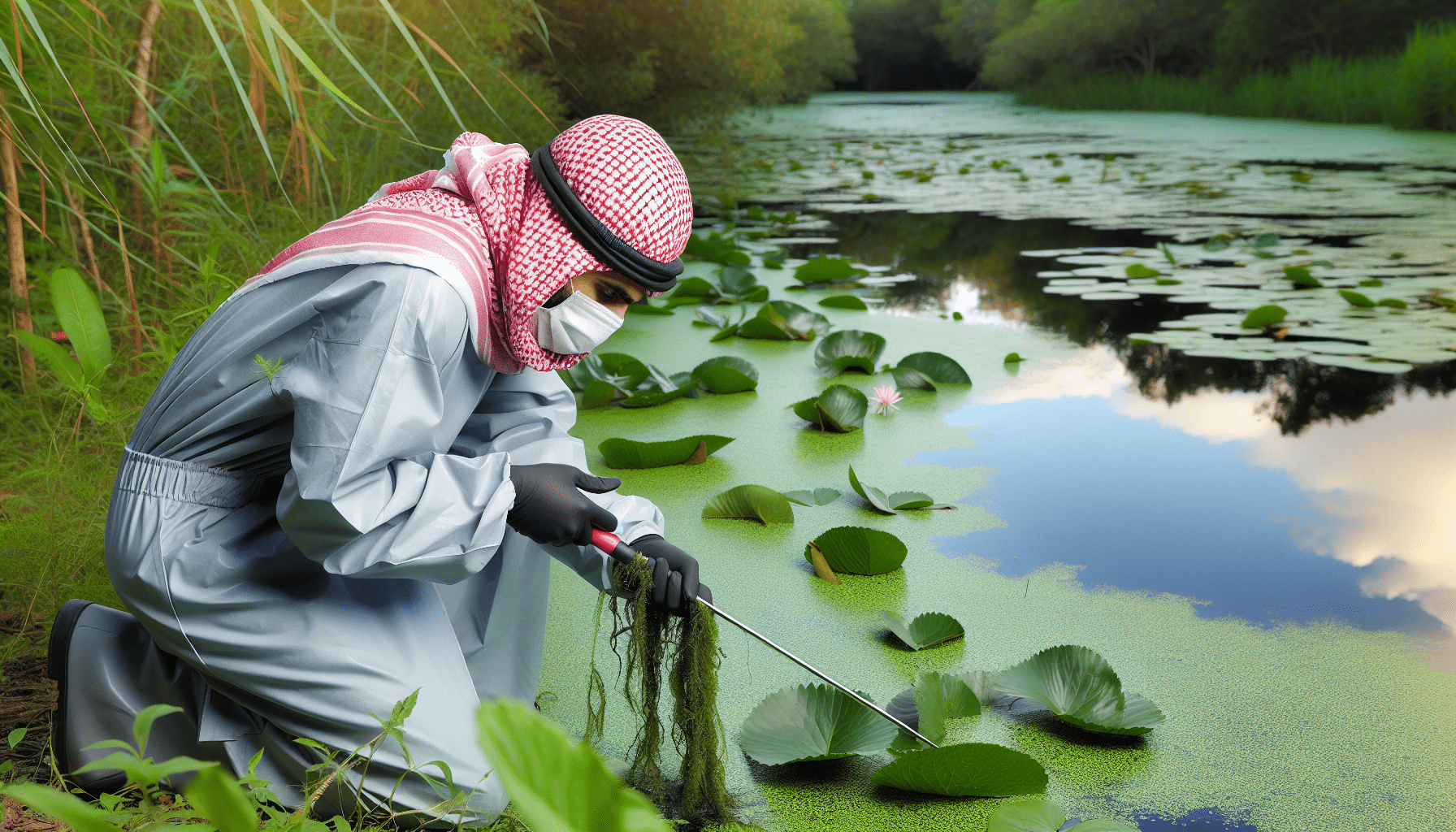
Dive into the essentials of maintaining your aquatic ecosystems with our guide, “How To Safely Remove Alligator Weed From Aquatic Environments.” In this article, you’ll discover practical and environmentally friendly methods to tackle the invasive alligator weed that threatens to disrupt your waterways. We’ll cover everything from manual removal techniques to understanding the best time for intervention, ensuring that you can protect your aquatic environment with confidence and care. Have you ever come across a mass of densely-packed, invasive plants choking your local pond or waterway, wondering how on earth you could safely remove it? If you’ve identified it as alligator weed, you’re likely grappling with a notorious invader that’s tough to control. But don’t worry—we’re here to help you navigate the challenge!
What is Alligator Weed?
Let’s start with getting to know your adversary. Alligator weed, scientifically known as Alternanthera philoxeroides, is a perennial herb originating from South America. This aggressive plant has become an invasive species in many parts of the world, particularly in aquatic environments.
Identification of Alligator Weed
First things first, you need to correctly identify alligator weed. This plant possesses:
- Leaves: Simple, opposite, and can be elliptic to lanceolate.
- Flowers: Small, white, and grow in clusters.
- Stem: Hollow, which allows it to float on water.
Incorrect identification can lead to ineffective or even harmful control methods, so it’s crucial to be sure.
Understanding the Risks
Before diving into removal techniques, it’s important to be aware of the risks that alligator weed poses.
Ecological Impact
Alligator weed can:
- Disrupt Native Vegetation: It grows rapidly, outcompeting native plants for sunlight and nutrients.
- Affect Wildlife: The dense matting it forms can hinder the movement of aquatic animals and reduce habitat quality.
- Water Quality Degradation: Its decaying mass can lead to decreased oxygen levels, negatively impacting aquatic life.
Health and Safety Issues
In some cases, alligator weed can:
- Harbor Pests: This aquatic nuisance can be a breeding ground for mosquitoes and other pests.
- Impair Recreational Activities: Its thick growth can obstruct water-based activities like boating or fishing.

Safe Removal Methods
So, how do you safely remove this invasive species? Different methods are available, each with its own set of pros and cons. Here’s a comprehensive guide designed to help you choose the best approach for your specific situation.
Manual Removal
Manual removal is labor-intensive but effective for small infestations.
Steps for Manual Removal
- Identify the Area: Mark the affected areas.
- Gather Equipment: You’ll need waterproof gloves, waders, and a rake.
- Physical Uprooting: Carefully pull the plants out, ensuring you remove as much of the root system as possible.
- Dispose of Material: Properly dispose of the weed. Do not leave any fragments nearby as they can quickly regrow.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Environmentally friendly | Labor-intensive |
| No chemicals required | Time-consuming |
| Effective for small areas | High risk of incomplete removal |
Mechanical Removal
Mechanical methods are more suitable for larger infestations but come with their own set of challenges.
Equipment Needed
- Aquatic Weed Harvester: Specialized machinery designed for aquatic plant removal.
- Excavators: For areas accessible by land, excavator buckets can remove large masses of weed.
Steps for Mechanical Removal
- Assessment: Survey the area to determine the best machinery and approach.
- Operation: Carefully use the machinery to extract the weed, ensuring minimal disturbance to surrounding habitats.
- Collection and Disposal: Gather and properly dispose of the extracted material to prevent regrowth.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Suitable for large areas | Expensive |
| Quick removal | Potential for habitat disruption |
| Reduces labor requirements | Requires specialized equipment |
Chemical Control
If manual and mechanical methods are not viable, chemical control is another option, though it should be used cautiously.
Suitable Herbicides
- Glyphosate: Non-selective herbicide effective against alligator weed.
- 2,4-D Amine: Selective herbicide, better for targeted control.
Application Steps
- Read Labels: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Prepare the Area: Ensure that no endangered species or protected habitats will be affected.
- Apply Carefully: Use protective gear and apply herbicides during dry conditions to prevent runoff.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Highly effective | Can harm non-target species |
| Suitable for large infestations | Risk of water pollution |
| Relatively quick results | Requires strict adherence to regulations |
Biological Control
A more environmentally-friendly, albeit slower, option is biological control, involving the use of natural predators.
Potential Biological Agents
- Agasicles hygrophila: A type of flea beetle that feeds on alligator weed.
- Vogtia malloi: A specific moth that targets alligator weed.
Steps for Biological Control
- Consult Experts: Always consult local environmental agencies before introducing biological agents.
- Release Agents: During optimal conditions, release the insects in the affected area.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Regularly check the progress and impact of the biological agents.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Environmentally friendly | Time-consuming |
| No chemicals involved | Requires careful monitoring |
| Sustainable long-term solution | Possible unforeseen ecological impacts |
Integrated Management Strategies
For effective long-term control, combining various methods often yields the best results. Here’s how you can develop an integrated management strategy.
Steps for Integrated Management
- Assess the Situation: Determine the size and severity of the infestation.
- Plan Your Approach: Develop a tailored plan using a combination of methods discussed above.
- Implement and Monitor: Consistently monitor the situation and be prepared to adjust your strategy as needed.
Example Strategy
For instance, you might start with mechanical removal of the densest areas, followed by manual clean-up of smaller patches, and finally, introduce biological agents to manage regrowth.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive and effective | Requires more planning |
| Adaptable to different situations | Can be resource-intensive |
| Long-term solution | Requires continuous monitoring |
Legal Considerations
Before you start removing alligator weed, note that there might be legal regulations concerning the treatment and disposal of invasive species.
Regulatory Agencies
- Local Environmental Agencies: Regulations can vary by location, so always consult your local guidelines.
- Permits: Some methods, especially chemical and biological controls, may require permits or special permissions.
Best Practices
- Documentation: Keep records of your control activities.
- Compliance: Ensure compliance with all legal and environmental regulations.
Community Involvement
Often, tackling an invasive species like alligator weed is more effective when the community comes together.
Educational Programs
Engage the community through workshops and seminars. Raise awareness about the problems posed by alligator weed and the best practices for its removal.
Volunteer Clean-up Events
Organize local clean-up events involving volunteers. These events can help address small infestations and raise public awareness.
Work with Local Authorities
Partnerships with local government bodies can provide additional resources and support for larger projects.

Evaluating Success
Finally, it’s crucial to evaluate the success of your removal efforts to ensure sustainable management of alligator weed.
Monitoring and Reporting
- Regular Inspections: Make periodic inspections of the treated areas.
- Data Collection: Compile data on regrowth rates, re-infestation, and the health of the aquatic environment.
- Adjust Strategies: Be prepared to tweak your methods based on the performance of your initial strategies.
Long-Term Management
Remember, removal is just one part of the process. Long-term management may involve continuous monitoring and periodic intervention to ensure the alligator weed does not return.
Conclusion
Removing alligator weed from aquatic environments is a significant task, but one that is entirely manageable with the right knowledge and tools. Whether you opt for manual, mechanical, chemical, or biological control—or a combination of these methods—understanding the pros and cons of each will help you make the best decision. Always consider the long-term impact on the ecosystem and comply with legal regulations. With diligent effort and community involvement, you’ll be well on your way to restoring balance to your local waterway.
Feel free to reach out with any questions or share your experiences tackling alligator weed—your insights could help others in their efforts! Happy weeding!

